[ad_1]
The extra I find out about ending, the extra I really feel the necessity to perceive precisely what’s going on in my finishes. Step one to understanding a end is often understanding the solvent wanted to work the end. I just lately discovered this text in our archives and thought it might assist some readers. It may be older, nevertheless it’s nonetheless comparatively updated and positively helpful in my store.
—Ben Strano
The alchemists of the Center Ages alternated their makes an attempt to transmute lead into gold with the seek for a common solvent—a liquid able to dissolving all supplies (had they succeeded, I ponder how they’d have packaged their discovery). 600 years later, I’m nonetheless following within the alchemists’ footsteps. As a chemist, I’m regularly requested to dilute a dish of gooey stuff or to dissolve some residue with out damaging the underlying materials. Woodworkers typically face related issues. Fortunately, if you already know slightly chemistry, you may choose a solvent that not solely does the job, but additionally poses the least well being and security hazards.
Regardless of the rising recognition of water-based finishes, in the end you will have to make use of one other solvent apart from water. Solvents work in considered one of two methods. Inert solvents, like mineral spirits and lacquer thinner, cut back the viscosity of finishes and permit deeper penetration, extra even utility, and quicker drying. They don’t alter the composition of the oils or resins used within the end. In distinction, reactive solvents assault the chemical construction of the supplies they dissolve; for instance, when methylene chloride is utilized to color, it turns into a paint stripper.
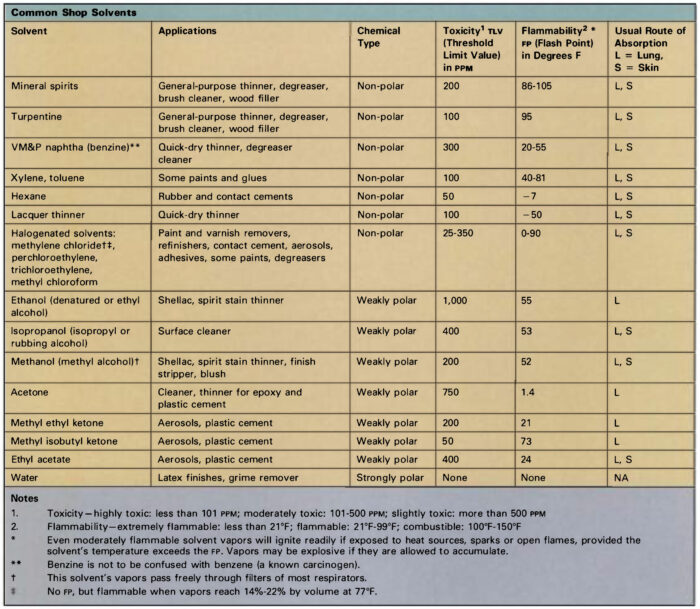
Many petroleum-based liquids can be utilized as thinners for brush-on varnishes and paints, and regardless that most of those natural solvents carry out equally, their toxicities differ broadly. The least hazardous alternative for brush-on varnish and paint thinner is mineral spirits. Turpentine additionally has low toxicity, nevertheless it’s extra more likely to trigger allergic pores and skin reactions. In truth, extended or repeated pores and skin publicity to most solvents (besides water) may cause pores and skin irritation. This happens as a result of many solvents, like acetone, ethanol, and ketones, extract pure oils from pores and skin layers, which leads to extreme chapping. In the event you want a thinner that dries shortly, naphtha is safer than most different fast-evaporating solvents, however bear in mind that quick-dry solvents all pose substantial fireplace hazards. Woodworkers are often shocked to be taught that probably the most flammable store solvent is acetone—a liquid that’s typically dealt with with little or no warning.
What’s in a label: Frequent solvents within the woodshop
Aliphatic hydrocarbons: Also called “paraffins,” these petroleum derivatives encompass chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Gaseous varieties embody methane, butane, and propane; molecules containing 5 or extra carbon atoms are liquid at room temperature. Pentane, hexane, heptane, and octane are main constituents of gasoline, kerosene, mineral spirits, and VM&P (varnish makers’ and painters’) naphtha. Hexane is broadly utilized in rubber-based liquids equivalent to contact cement and rubber cement. Isobutane and propane function propellants in some spray cans.
Aliphatic solvents are typically much less poisonous than different courses of natural liquids, although they don’t seem to be risk-free. Frequent signs ensuing from extreme publicity embody pores and skin and respiratory irritation and central nervous system (CNS) melancholy.
Fragrant hydrocarbons: These compounds are ring-shaped molecules distilled from coal tar. These liquids are highly effective solvents, however their use is proscribed by low flash-points, excessive volatility, and excessive toxicity. Three compounds are frequent: Toluene (toluol) and xylene (xylol) are sometimes added to aliphatic solvents to extend their effectiveness. Benzene will not be utilized in most areas, owing to its excessive toxicity and carcinogenic properties, however it’s generally current in small quantities as a contaminant in commercial-grade solvents. Benzene is often confused with benzine, an alternate identify for VM&P naphtha, quite a lot of mineral spirits.
Alcohols: Denatured ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is broadly used as a solvent for shellac, and consists of grain alcohol made toxic to drink by the addition of methyl alcohol or another poisonous liquid. Methyl alcohol (methanol, “wooden alcohol”) is utilized in lacquer thinner, paint remover, shellac, and aniline-based wooden stains. Methyl alcohol will be absorbed by way of the pores and skin and its vapors are way more poisonous than these of denatured alcohol, so the latter product ought to be employed for common store use.
Ketones and esters: This group contains plenty of compounds which include oxygen in addition to carbon and hydrogen. Ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, and amyl acetate are esters utilized in nitrocellulose lacquer. Frequent ketones embody acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, and methyl isobutyl ketone. Esters and ketones usually have sturdy odors and excessive flammability. They’re significantly more likely to irritate the pores and skin due to their means to dissolve pure oils, they usually could produce respiratory irritation and signs of CNS melancholy. A ketone by-product, methyl ethyl ketone peroxide, is used as a catalyst for polyester resins. This sturdy oxidizing agent will trigger critical harm to the pores and skin and eyes, and calls for cautious dealing with.
Glycol ethers: These are one other kind of oxygenated natural compound utilized in solvents, mostly in sluggish drying lacquer. Glycol ethers are extremely poisonous, and may trigger liver, kidney, and CNS harm. As well as, they might adversely have an effect on reproductive organs, inflicting delivery defects and miscarriages.
Mineral spirits (VM&P naphtha, white spirits): These are distilled from petroleum, and consist principally of the aliphatic hydrocarbons hexane, heptane, and octane. Composition varies in keeping with the supply of the crude oil and manufacturing variations from batch to batch, and chemical evaluation reveals the presence of as many as 100 separate compounds in some samples. Mineral spirits are grouped into three classes:
- Odorless: Low-boiling-point ( 140°-180ºF) “odorless” spirits consist principally of aliphatic compounds with quick evaporation charges and comparatively weak solvency.
- Low odor: Medium- boiling-point (200° to 300°F) “low odor” spirits are predominantly heptane and octane fortified with small quantities of xylene and toluene.
- Common odor: Excessive boiling level (300° to 400° F) “low odor” mineral spirits comprise about 75% of all solvents used within the paint business. They encompass 15% to 25% fragrant hydrocarbons.
Mineral spirits are much less poisonous than most different solvents, however vapors may cause pores and skin and respiratory irritation and CNS melancholy. Toxicity will increase in proportion to the fragrant hydrocarbon content material, so odorless spirits are finest for common use.
Turpentine: That is produced by steam distillation of pine gum, and consists principally of carbon-ring compounds known as turpenes. Pine gum comprises about 68% strong rosin, 20% turpentine, and 12% water. Turpentine has a robust, attribute odor, however its bodily properties are similar to mineral spirits, which has largely changed it as a solvent. Turpentine is extra chemically reactive, and can discolor upon lengthy publicity to mild or to air. Its vapors may cause respiratory irritation in addition to dizziness, headache, and different indicators of CNS melancholy. It’s a sturdy pores and skin irritant, and may trigger extreme allergic reactions after repeated contact.
Lacquer thinner: Lacquers are often made by dissolving a cellulose by-product in an appropriate solvent, although trendy formulations could embody alkyd resin, pure rosin, or different dissolved solids. Lacquer thinner makes use of about 30% esters and ketones because the energetic solvent, diluted with fragrant and aliphatic hydrocarbons. The ester, ketone, and fragrant content material makes these solvents very risky and comparatively poisonous, so they need to be used solely when wanted and never as a common substitute for mineral spirits when thinning liquids or cleansing brushes.
-George Mustoe
Excerpted from articles in Nice Woodworking #41 and #92
Disposing of solvents responsiblyAs woodworkers, we use solvents and ending merchandise that find yourself as hazardous wastes, so it’s necessary to maintain abreast of environmentally accountable waste-disposal strategies. The Code of Federal Laws (Title 40-Safety of the Atmosphere) defines hazardous waste and establishes reportable portions for releases of sure chemical compounds. Nevertheless, these legal guidelines don’t apply to most woodworkers as a result of they use such small quantities of natural compounds, equivalent to solvents. Nonetheless, even small portions of hazardous wastes can contaminate the atmosphere. A quart of stripper carelessly discarded in a stream can contaminate thousands and thousands of gallons of water. However there are some secure methods to get rid of small quantities of hazardous waste, as follows:
-Jeff Jackson is an environmental engineer and part-time woodworker residing in Taylors, S.C. From Nice Woodworking #92 |
Join eletters immediately and get the newest strategies and how-to from Nice Woodworking, plus particular provides.
[ad_2]